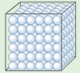
 Solids contain particles that are attracted to each other by strong forces. These forces cause the particles to arrange themselves in a closely packed pattern. These particles vibrate, but do not change position. The attractive forces among the particles of a solid are strong enough to hold these particles together in a fixed position within the solid and thus maintain the solid in a definite shape.
Solids contain particles that are attracted to each other by strong forces. These forces cause the particles to arrange themselves in a closely packed pattern. These particles vibrate, but do not change position. The attractive forces among the particles of a solid are strong enough to hold these particles together in a fixed position within the solid and thus maintain the solid in a definite shape. Liquids contain strong forces of attraction between their particles. They are closely packed but not in a pattern. These particles are constantly moving and so the particles change their position. The attractive forces among the ultimate particles of a liquid are sufficiently strong enough to hold them together but are not strong enough to hold them in a fixed position.
Liquids contain strong forces of attraction between their particles. They are closely packed but not in a pattern. These particles are constantly moving and so the particles change their position. The attractive forces among the ultimate particles of a liquid are sufficiently strong enough to hold them together but are not strong enough to hold them in a fixed position. Gases have weak forces of attraction between the particles. These particles have a lot of kinetic (movement) energy. They are in constant random motion. The particles are far apart (essentially independent of each other) and are not fixed in a pattern. Thus , gas is everywhere.
Gases have weak forces of attraction between the particles. These particles have a lot of kinetic (movement) energy. They are in constant random motion. The particles are far apart (essentially independent of each other) and are not fixed in a pattern. Thus , gas is everywhere.Related Articles:
What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter?
How does sound travel?
What is Sound?
No comments:
Post a Comment